#1. Which of the ones listed would be the best at cleaning off the grease?
#2. Which one would be second best?

#3. Using
the rule of LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE, which of the following left outside
would get dissolved by rain and end up in your well water.
Candle wax
Sugar
Salt (sodium chloride)
Drywall (CaSO4) (hint Ca=+2 charge, SO4=-2 charge)
Lead (II) Chloride
Sodium Fluoride
Plastic bottles
Glass bottles
Alcohol
#4. Why is the surface tension of water reduced when the soap is present?

#5. In the nutritional facts section, which ones are the electrolytes?
#6. In the ingredients section, which ingredients contain electrolytes? (exclude flavoring and color)

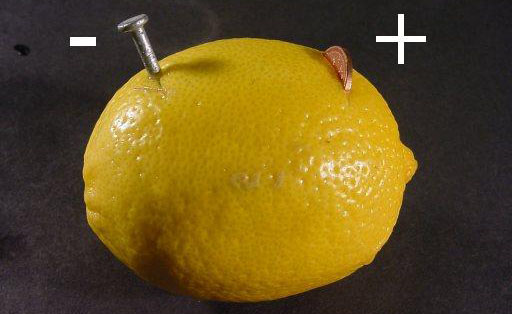

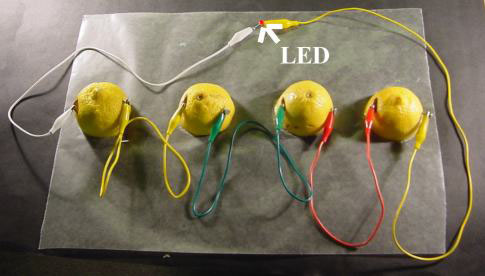
Pictures from EMR Labs, LLC
To the left is a lemon turned into a battery using a copper coin and a zinc plated nail (galvanized nail).
The second image is the lemon battery voltage being checked. It shows that it is 0.906 volts. If you can get over 3 volts, you can light up an LED.
The bottom image shows that 4 lemons are put in series to boost the voltage to 3.624 volts (4 x 0.906 volts). This will light up the LED. For current to flow, there needs to be an electrolyte in the lemons. There is an acid that is in lemons that acts as the electrolyte which can carry the charge.
#8. What is that acid?
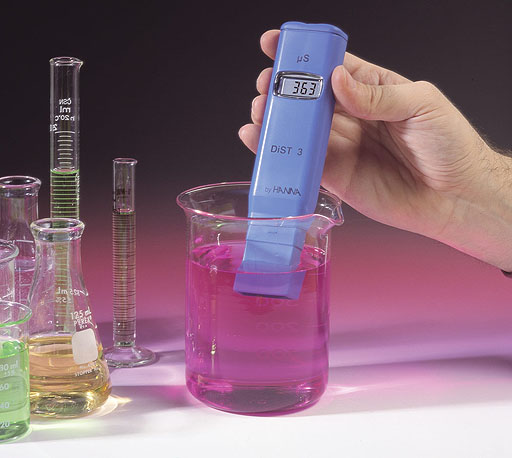

#9. What is 363 microsiemens written in just siemens?
#10. If some table salt (NaCl) was added to the beaker being shown, what change would it make to the reading?
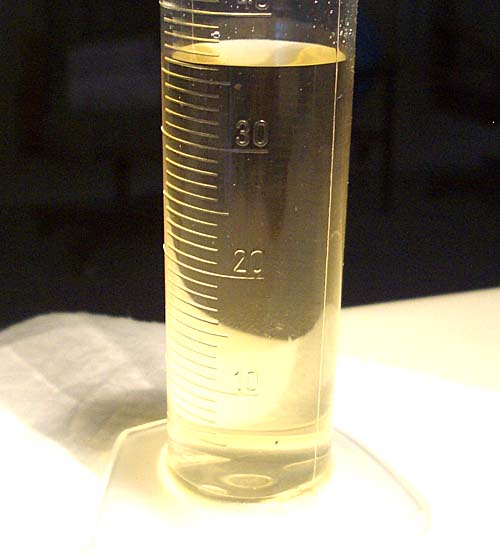


In the tutorial I mentioned that water is attracted to glass, so you get a curved surface (a meniscus) See glass graduated cylinder (top image).
The below graduated cylinder does not have a meniscus, which means it is not attracted to the inside walls of the graduated cylinder. That's because this graduated cylinder is made from plastic rather than glass.
#11. If you measured the volume of some vegetable oil in a glass graduated cylinder, would you see a meniscus or not?

#12a. The image on the left shows a sewing needle floating on water. How is that possible?
#12b. Could the needle float on rubbing alcohol?

#13. Why is an ethanol safer than gasoline with regards to putting out the fire with water?
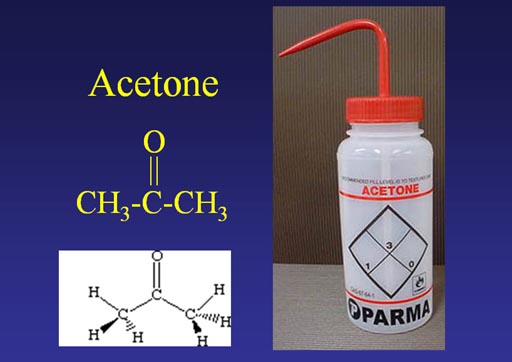
Water is dissolved by acetone. In other words, if you want some glassware to dry faster, rinse the water off with acetone. If water dissolves in acetone, it must be attracted to the acetone in some way.
#14. What atom or atoms in the acetone is water attracted to?

#15. If you had just a saturated solution of sodium acetate, how can you turn it into a supersaturated solution?
A magic trick is also done using supersaturated sodium acetate.
The magicians have a little powdered sodium acetate on their fingers. When they snap their fingers above a supersaturated solution of sodium acetate, the solution instantly starts to crystallize and becomes a solid in seconds. It looks like magic.
#16. Why did snapping the fingers cause the solution to crystallize?

When I want to know the solubility
of different substances in water or some other solvent, I turn to the CRC
Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. This reference book indicates the solubility
of many inorganic and organic compounds. This book is online but requires a subscription. An alternative is Wikipedia, which does list the solubility of many compounds.
#17. Report what is the solubility in water of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin).
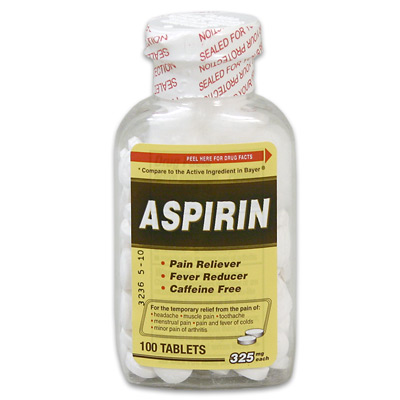
#18. Aspirin tables often contain 325 mg of aspirin each. Using the solubility you found in Wikipedia, how much water is needed to dissolve 2 tablets at 20°C (room temperature)?
#19. If you used hot water, could you dissolve more or less aspirin in that same amount of water?

#20. What is that in molarity (moles per liter)?

Here we have Crest toothpaste. They list two concentrations. One is for sodium fluoride (0.243% w/v and one is for just the fluoride ion (0.15% w/v). So that translates to 0.243 grams of NaF per 100mL of toothpaste and 0.15 grams of F- per 100mL of toothpaste.
#21. What is the molar concentration of NaF?
#22. What is the molar concentration of the fluoride ion?

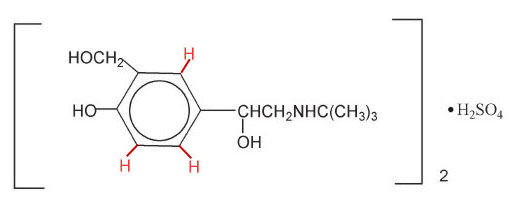
Changing this to moles per liter requires you to know the molar mass of albuterol sulfate. Below this image is the structural formula of albuterol sulfate. The "·H2SO4" to the right of a bracket with a subscript of 2, means one molecule of sulfuric acid sits between two molecules of albuterol. To find molar mass we need to total up all carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms. The hexagon on the left with the ring inside means this is a benzene ring where there normally are 6 carbon and 6 hydrogen atoms. The red hydrogen atoms are not normally shown. (Hint: Wikipedia has molar mass of albuterol. Double that and add the molar mass of sulfuric acid, or you can add all atomic masses yourself).
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
|
| 1 | milli units (m) cancel | Convert to moles using molar mass |
|||||
| 2 | 5 |
mg | 1 |
mole |
= | ??? | moles |
| 3 | 1 |
mL | ??? |
grams | Liter | ||
#24. What is the molarity of albuterol sulfate in a 0.5% solution (F2)?

In the tutorial I mentioned that 42 grams of MTBE additive will dissolve in a liter of water. That means a saturated solution of MTBE is 42g/L). I also said that at the concentration of 0.0001grams per liter or higher it can be tasted. A report said that a water truck with 2500 gallons of water that was saturated with MTBE got dumped into the lake used for community water. The lake is 8.25 acres and 10.5 feet average depth.
#25. What will be the concentration of MTBE in the lake in grams per liter (2 sig figs)? (See below for setup)
#26. Also, will people taste the MTBE? (If greater than 0.0001g/L, then yes.)
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
|
| 1 | 2500 |
gallons | 1 |
acre-feet | = |
0.00767 |
acre-feet | truck volume | |||||
| 2 | 325851 |
gallons | 86.625 |
acre-feet | add lake volume | ||||||||
| 3 | 86.633 |
acre-feet | Total volume | ||||||||||
| 4 | concentration |
x volume |
Only grams left |
divide by new volume |
change volume to liters |
final concentration | |||||||
| 5 | 42 |
g | 2500 |
gallons | 3.785 |
liters | 1 |
acre-feet | = | ???? |
grams | ||
| 6 | 1 |
liter | 1 |
gallon | 86.633 |
acre-feet | 1233481 |
Liters | Liter | ||||
#27. In rows 5 and 6, what units cancel?
#28. In rows 5 and 6, what units don't cancel?
#29. What is the spreadsheet formula that goes into L5?

Here's a label on an Abolut Vodka bottle. Instead of saying "by Vol" they just used "/Vol."
#30. How many milliliters of ethanol is in this bottle?

Here's a 0.1 molar solution of sodium arsenate. That means 0.1 moles per liter. Because of the arsenic in it, it is quite poisonous. Notice the health warning is "4", which is the highest danger level.
Use the atomic number of your element code name as the number of milliliters of a sample taken from this solution. For example, if your element code name was Niobium, your atomic number would be 41. So that person would use 41 mL. You use the atomic number of your own element code name for the mL.
#31. How many moles of sodium arsenate are in your sample?
#32. How many grams of sodium arsenate are in your sample?
#33. If the lethal dose is 200mg per kg body weight. Would your sample kill a 100 kg (220 lb) person?

Here is 0.1M (0.1 moles per liter) of
sodium phosphate.
#34. This bottle has 2.2 liters
of solution. How many moles of sodium phosphate are in those 2.2 liters?
#35. How many moles of sodium ions are those 2.2 liters?
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
|
| 1 | Molar Concentration |
times volume in liters |
Gives moles |
||||
| 2 | 0.1 |
moles Na3PO4 | 2.2 |
liters | = |
?? |
moles Na3PO4 |
| 3 | liter | ||||||

You are working in a rural clinic where
you have to make up your own IV solutions. You are asked to make up a
4.0 liters of 10% w/v solution from this anhydrous Dextrose.
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
|
| 1 | |||||||||||
| 2 | 10 |
% w/v | = |
10 |
g |
4.0 |
Liters |
milli |
= |
??? |
g dextrose |
| 3 | ??? |
mL |
??? |
#36. What goes in D3?
#37. What goes in H3?
#38. How many grams do you weigh out (J2)?
#39. What units cancel in the calculations above?

Let's say you had a nursing assistant make up the 10% dextrose IV bags. The instructions for each bag were to weigh out 100 grams of dextrose and dissolve it in a liter. He did that. Later you find out that he thought you said "sucrose" not "dextrose" and made up some bags using 100 grams of sucrose instead. Those bags got mixed in with the proper dextrose bags. One trick in telling them apart is to put them all in a freezer and see which ones freeze first. Both sugars will keep water from freezing at 0°C, but the bags that have the higher moles of sugar will require a colder temperature to freeze.
#40. 100 grams of dextrose is how many moles? (Note: dextrose formula is C6H12O6)
#41. 100 grams of sucrose is how many moles? (Note: sucrose formula is C12H22O11)
The bags that have the most moles will freeze last (require a lower temperature).
#42. Which bags will freeze last?